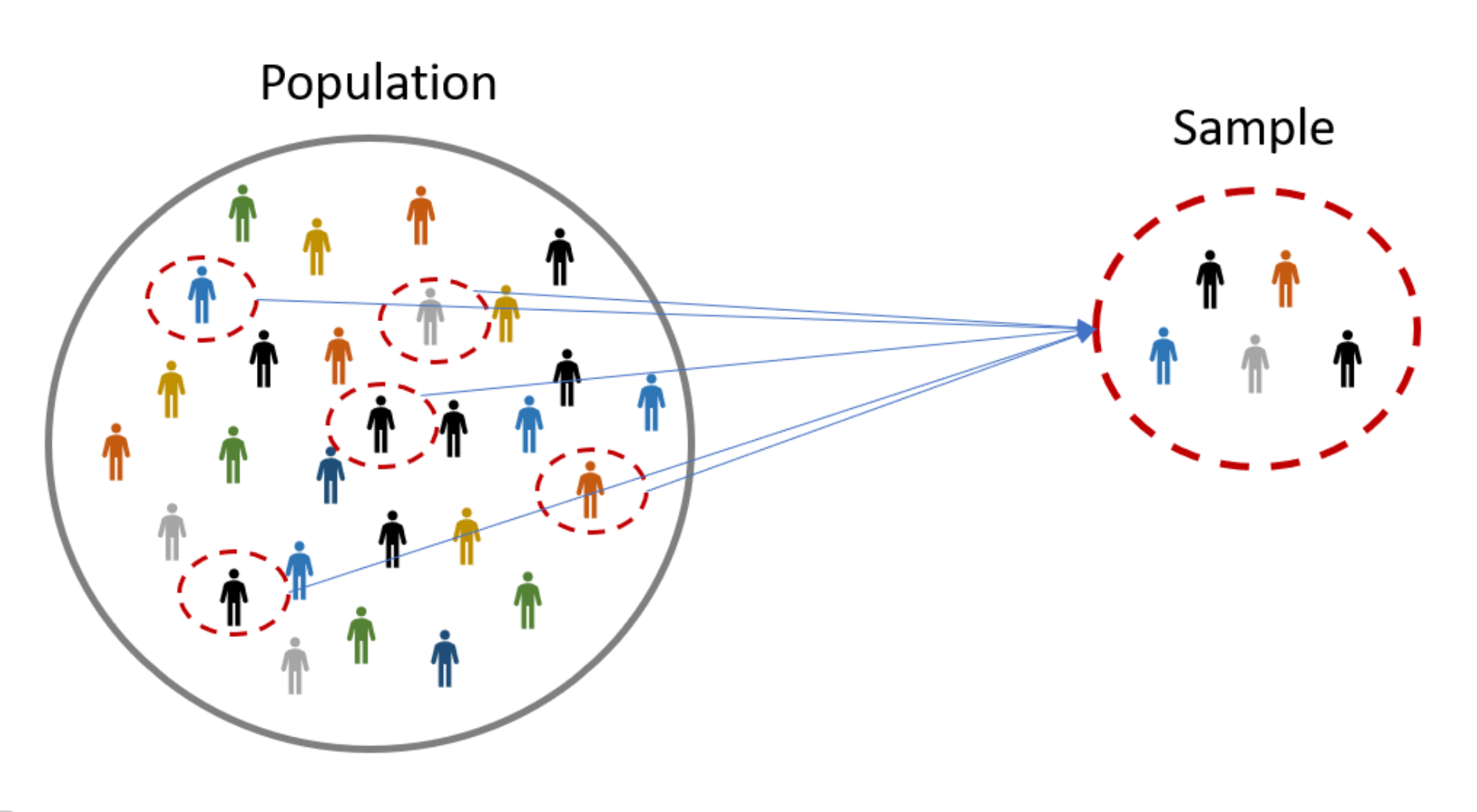
Instead, we select a sample. The sample is the group of individuals who will actually participate in the research.
Definition of Sampling?
Difference between population and sample?
Understand the difference between a population and a sample:
- The population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about.
- The sample is the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from.
The
population can be defined in terms of geographical location, age, income, or
many other characteristics.
Types of Sampling Method?
There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research:
- Probability Sampling
- Non-Probability Sampling
The main difference between probability and non-probability sampling is how the sample is selected from the population. Probability sampling is based on random selection, while non-probability sampling is based on non-random criteria. Probability sampling is considered more reliable and unbiased, while non-probability sampling is deemed less reliable and less fair.
What is Probability Sampling?
Probability
sampling is a type of sampling where every member of the population has an
equal chance of being selected for the sample. Probability sampling is
considered the most reliable and unbiased method because it ensures that the
sample is representative of the population and reduces the potential for bias. This
method is more time-consuming and expensive than the non-probability sampling
method.
Types of
Probability Sampling?
Probability Sampling methods are further classified into different types:
- Simple random sampling
- Systematic sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Clustered sampling
What is
Non-Probability Sampling?
The
non-probability sampling method is a technique in which the researcher selects
the sample based on subjective judgment rather than random selection. In
this method, not all the members of the population have a chance to participate
in the study.
Types of Non-Probability
Sampling?
Non-Probability
Sampling methods are further classified into different types:
- Convenience Sampling
- Consecutive Sampling
- Quota Sampling
- Purposive or Judgmental Sampling
- Snowball Sampling
Benefits of Sampling in Quality Management:
Cost-effective:
Sampling is a cost-effective approach to quality management,
as it allows organizations to inspect or test a subset of products or services
rather than the entire population. This approach reduces the time and resources
required for quality control.
Efficient:
Sampling is an efficient approach to quality management, as
it enables organizations to assess the quality of products or services quickly
and accurately. This approach is especially useful when dealing with large
populations, where inspecting or testing each item is not feasible.
Reliable:
Sampling is a reliable approach to quality management, as it
provides a statistically valid representation of the population. This approach
ensures that the sample accurately reflects the quality of the entire
population.
Conclusion:
Sampling is a vital tool in quality management that enables
organizations to assess the quality of their products or services effectively
and efficiently. By selecting a representative sample from a larger population,
organizations can identify defects or non-conformance and take corrective
actions to prevent their recurrence. The use of sampling in quality management
can help organizations to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve the
reliability of their products or services.